
Understanding Property Attributes in Application Maps

Understanding Property Attributes in Application Maps
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Registration
- Using Advanced Installer
- GUI
- Working with Projects
- Installer Project
* Product Information
* Resources
* Package Definition
* Requirements
* User Interface
* System Changes
* Server
* Internet Information Services Page”)
* IIS Server
* Global Settings
* Website Settings
* Physical Path Credentials Dialog
* Web Site Bindings/SSL Settings
* Virtual Directory Settings
* ASP.NET Settings
* Access Flags
* Authentication
* Default Document
* Website Performance
* FTP Access
* FastCGI Settings
* ISAPI Filters
* MIME Types
* Application Mapping
* Application Mapping Properties
* HTTP Response Headers
* Machine Key
* HTTP Error Handling
* .NET Error Handling
* Custom Properties
* Application Pools
* Web Deploy Packages
* Legacy Options
* IIS Browse
* ODBC
* SQL Databases
* SharePoint Page
* Silverlight Page
* Custom Behavior - Patch Project
- Merge Module Project
- Updates Configuration Project
- Windows Store App Project
- Modification Package Project
- Optional Package Project
- Windows Mobile CAB Projects
- Visual Studio Extension Project
- Software Installer Wizards - Advanced Installer
- Visual Studio integration
- Alternative to AdminStudio/Wise
- Replace Wise
- Migrating from Visual Studio Installer
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Shell Integration
- Command Line
- Advanced Installer PowerShell Automation Interfaces
- Features and Functionality
- Tutorials
- Samples
- How-tos
- FAQs
- Windows Installer
- Deployment Technologies
- IT Pro
- MSIX
- Video Tutorials
- Advanced Installer Blog
- Table of Contents
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
Application Mapping Properties
This view allows you to map a certain web document type to a desired script processor that can handle the corresponding script type.
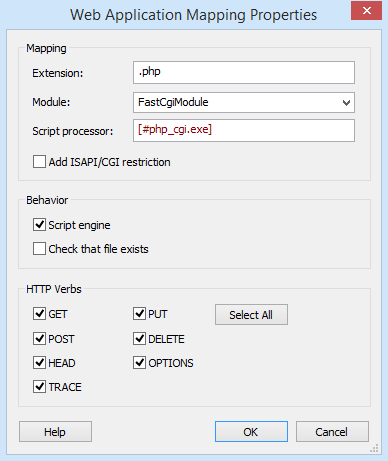
Mapping
Extension
You can set the web document extension to be mapped to this script processor.
You can configure wildcard script maps by setting the extension field to: * .
Module
In this field you can specify the module handler for your application mapping. This field is of Formatted Type .
When this field is empty, the Application Mapping will be deployed on all IIS versions. However, when a module value is present, deployment of that Application Mapping will be done only on IIS 7.0 and newer.
For ISAPI/CGI Script Maps, IIS 7 requires CgiModule/IsapiModule to be set as the ScriptMap’s module. The user can do this from our UI but, because of the rule described above, will have the Application Mapping deployed only to IIS 7.0 and newer. However, if the script processor path ends with ‘.exe’/‘.cgi’/‘.dll’ then the correspondent module will be added automatically to the mapping on IIS7 and newer. Thus leaving the module field empty for such ISAPI/CGI Script Maps guarantees that the script will be deployed on all IIS versions.
Script Processor
You can set the script processor file for the new web application mapping. The file can be from the installation package or external. This field is of Formatted Type and can be edited with the Smart Edit Control .
Add ISAPI/CGI Restriction
Allows dynamic content to execute on the target IIS server.
On IIS 6 the feature is called Web Service Extensions.
Behavior
Script engine
Select this option when you want the application to run in a directory without Execute permissions. This setting is intended primarily for script-based applications such as ASP and IDC that are mapped to an interpreter.
Check that file exists
Select this option to instruct the Web server to verify the existence of the requested script file and to ensure that the requesting user has access permission for that script file.
If the script does not exist or the user does not have permission, the appropriate warning message is returned to the browser and the script engine is not invoked. This option can be useful for scripts mapped to non-CGI executables like the Perl interpreter that do not send a CGI response if the script is not accessible.
Because the script will be opened twice, once by the server and once by the script engine, there is some performance cost to enabling this option.
HTTP Verbs
Allows you to set the HTTP verbs that should be passed to an application.
These verbs are: GET, POST, HEAD, TRACE, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS.
For a detailed explanation of these HTTP/1.1 methods please see:HTTP Methods article.
Did you find this page useful?
Please give it a rating:
Thanks!
Report a problem on this page
Information is incorrect or missing
Information is unclear or confusing
Something else
Can you tell us what’s wrong?
Send message
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved Twitter Video Requirement - Aspect Ratio
- [New] In 2024, PickUp or Something Else? Unveiling Best Android Photo Editor
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Unveiling the Secrets to Effective MacBook Air Screen Capture
- [Updated] From Live Chat to Large Screen Upload Twitch Streams to YouTube for 2024
- [Updated] In 2024, How to Merge/Combine/Join YouTube (FLV) Videos
- Efficient Software Component for Regular Updates: IUpdaterComponent Explained
- In 2024, 3 Ways to Fake GPS Without Root On Nubia Z50S Pro | Dr.fone
- Manage Your Profile: Detailed Guide to Navigating Account Preferences
- Mastering Cross-Platform Gaming: A Guide to Playing Your Favorite iPhone Titles on a Computer or Mac
- Maximize Valheim Play Experience: 2024'S Ultimate Fixes for Frame Rate Drops
- Possible solutions to restore deleted call logs from Realme
- Premium Gratis Image Cleaner: Top Watermark Stripper Apps
- Simple Techniques for Watermark Removal From 2021 Videos
- Streamline Your Event Planning with Advanced Editing Tools and Features
- User-Friendly File Download Prompt Guide
- Title: Understanding Property Attributes in Application Maps
- Author: David
- Created at : 2024-10-07 01:59:47
- Updated at : 2024-10-10 19:34:36
- Link: https://fox-zaraz.techidaily.com/understanding-property-attributes-in-application-maps/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.